
ZFS, the short form of Zettabyte Filesystem is an advanced and highly scalable filesystem. It was originally developed by Sun Microsystems and is now part of the OpenZFS project.
ZFS is a 128-bit filesystem and has the capacity to store 256 zetta bytes!
Terminology
Before we move on, let us understand some of the terminologies that are commonly used in ZFS.
Pool
Logical grouping of storage drives. It is the basic building block of ZFS and it is from here that storage space gets allocated for datasets.Datasets
The components of ZFS filesystem namely filesystem, clones, snapshots and volumes are referred to as datasets.Mirror
A virtual device storing identical data copies on two or more disks. In situations where one disk fails, same data is available on other disks of that mirror.Resilvering
Process of copying data from one disk to another in the event of restoring a device.Scrub
Datasets
Scrub is used for consistency check in ZFS like how fsck is used in other filesystems.
The components of ZFS filesystem namely filesystem, clones, snapshots and volumes are referred to as datasets.
Installing ZFS
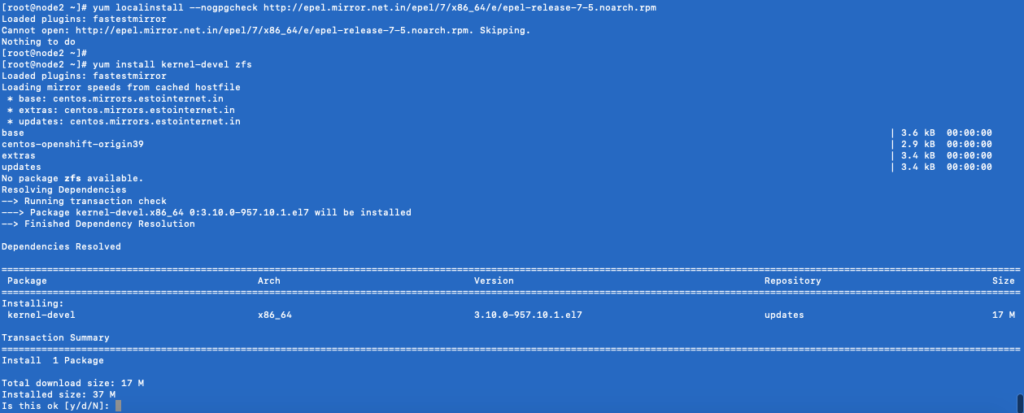
# yum localinstall –nogpgcheck http://archive.zfsonlinux.org/epel/zfs-release.el7.noarch.rpm
# yum install kernel-devel zfs
Verify if the zfs module is inserted into the kernel
# lsmod |grep zfs
# zfs list
ZFS has two main utilities, zpool and zfs. While zpool deals with creation and maintenance of pools using disks zfs utility is responsible for creation and maintenance of datasets.
Creating Pools
First verify the disks available for you to create a storage pool.
#ls -l /dev/sd*
Create a pool from a set of drives.
#zpool create <option> <pool name. <drive 1> <drive 2>

(Run this command to create POOL)
# zpool status
***************************
Next Blog is Coming Soon on ZFS Mirroring and ZFS File System —-
